Pilot Group – Dosimetry in nuclear medicine
-

Chairperson
Weibo Li
German Federal Office for Radiation Protection (BfS)
Email: wli [at] bfs [dot] de (wli[at]bfs[dot]de) -

Secretary
Lara Struelens
SCK CEN, Belgium
Email: lara [dot] struelens [at] sckcen [dot] be (lara[dot]struelens[at]sckcen[dot]be) -

Membership
The Pilot Group has:
- 20 full members,
- approx. 20 corresponding members and
- approx. 20 observers.
Liaisons
The Pilot Group has 4 liaisons from EANM - Silvano Gnesin (Dosimetry) and Elena Prieto (Radiation Protection), SIG-FRID - Manuel Bardiès and ICRP - Augusto Giussani.
Motivation
Nuclear medicine is a specialized discipline of medicine administering radionuclides and compounds to diagnose and treat various diseases and cancers. There are about 35 million patients worldwide, of which 9 million in Europe, receiving nuclear medical procedures every year. Advanced molecular imaging technologies, such as PET and SPECT, together with CT and MRI are able to detect tumors and diseases online for further treatment. In addition to the benefit of the treatments, the radiation dose is a fundamental quantity for radiation protection, risk assessment and treatment planning to the patients, medical staff and the public, and the environment. EURADOS has many years of experience about the radiation protection in medicine. EURADOS has embarked on several projects with other nuclear medicine associations since its establishment in the 1980s’. As a result of the EURADOS strategic research agenda (SRA) 2020, the nuclear medicine dosimetry was identified and put as a solid and independent challenge parallel to the radiation therapy and medical imaging dosimetry for the next decades. Concurrently, radiopharmaceutical therapy in nuclear medicine is undergoing a renaissance and the EC Directive 2013/59/Euratom states in article 56 that exposures of target volumes in nuclear medicine treatments shall be individually planned. The EURADOS pilot group aims to develop patient dosimetry methods and monitoring radiation exposure and engage in radiation protection in the nuclear medicine research field together with international and European associations.
Aim of the Working Group:
To improve radiation protection and patient dosimetry in nuclear medicine by optimizing diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
Task Group
-
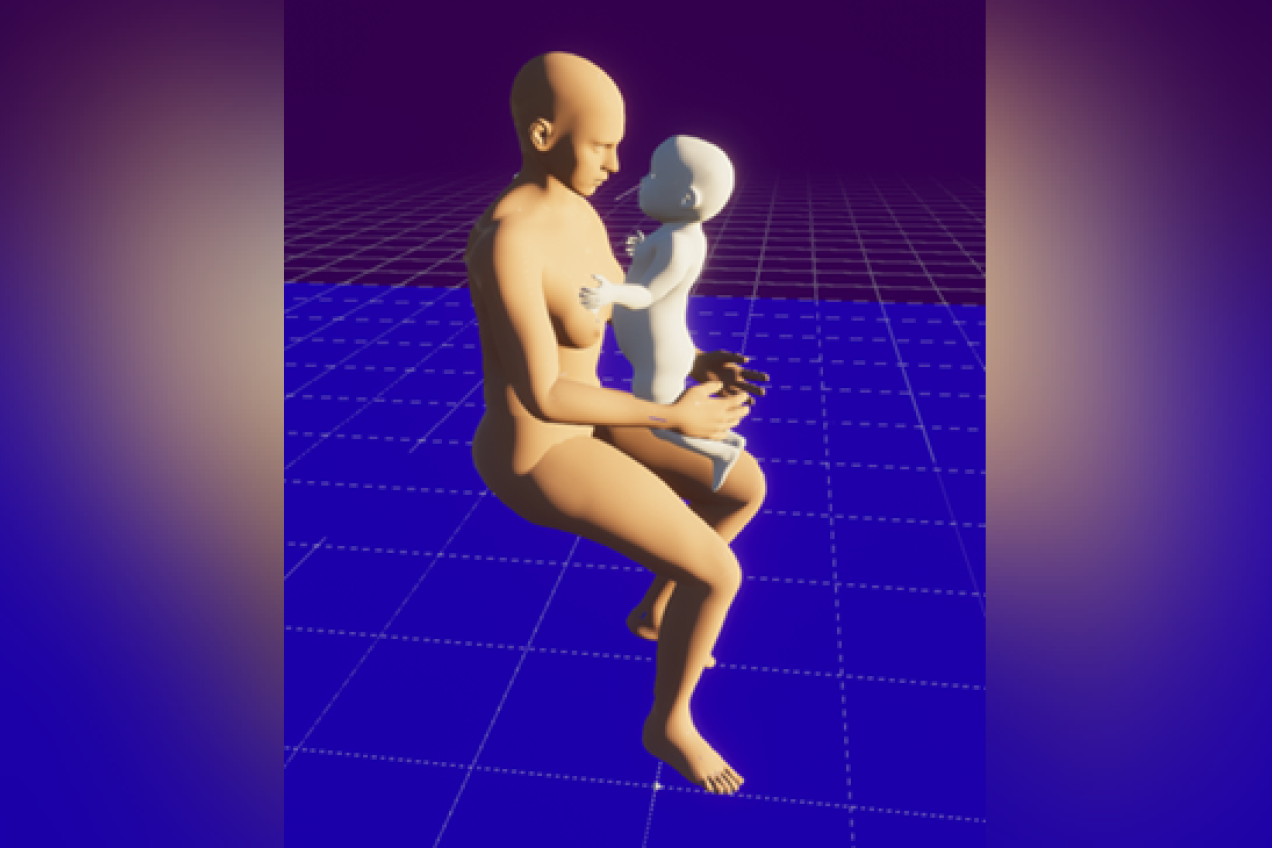

TG1 External dose rates from nuclear medicine patients to caregivers
Task Group leader: Lara Struelens (SCK CEN, Belgium)
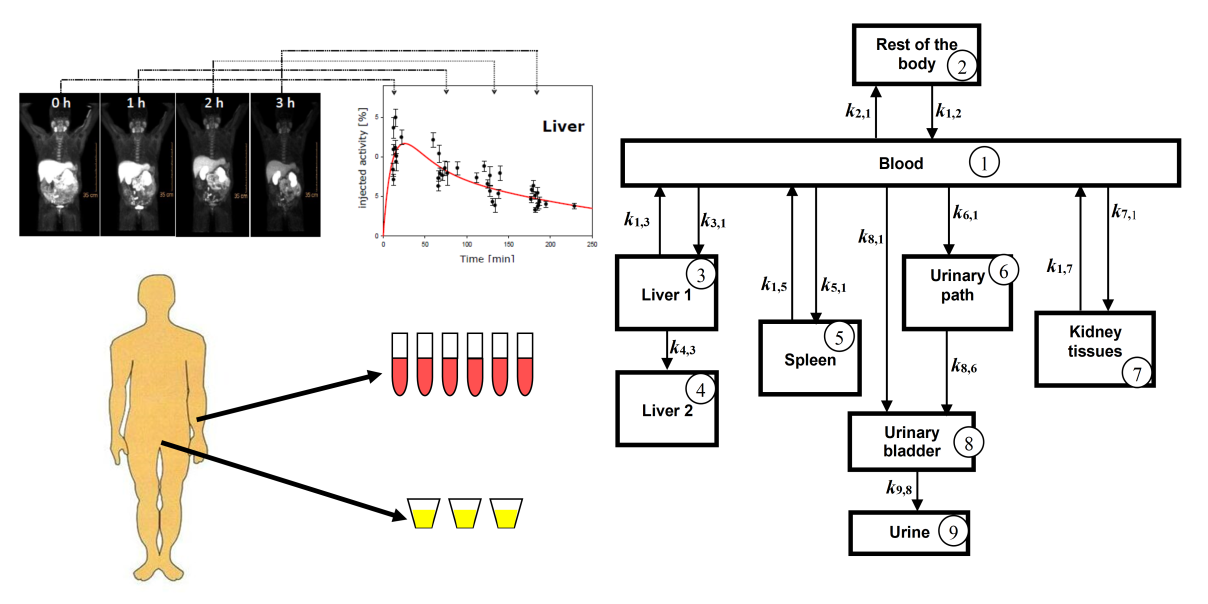
The growing use of nuclear medicine and the diversity of new radiopharmaceuticals, stimulate the need for a more comprehensive re-evaluation of the radiological risk for caregivers and general public coming into proximity of nuclear medicine patients. The objective of this task is to develop a more comprehensive dose calculation approach by using the most recent advancements in computational dosimetry, such as Monte Carlo simulations, realistic flexible human phantoms, and time activity distribution curves from the most recent biokinetic models. In addition to caregiver and medical staff dose assessment, this new dose calculation framework is particularly important for modelling some of the most concerning close contact exposure situations, such as an adult holding/comforting a child patient, or a mother breastfeeding her child.
-
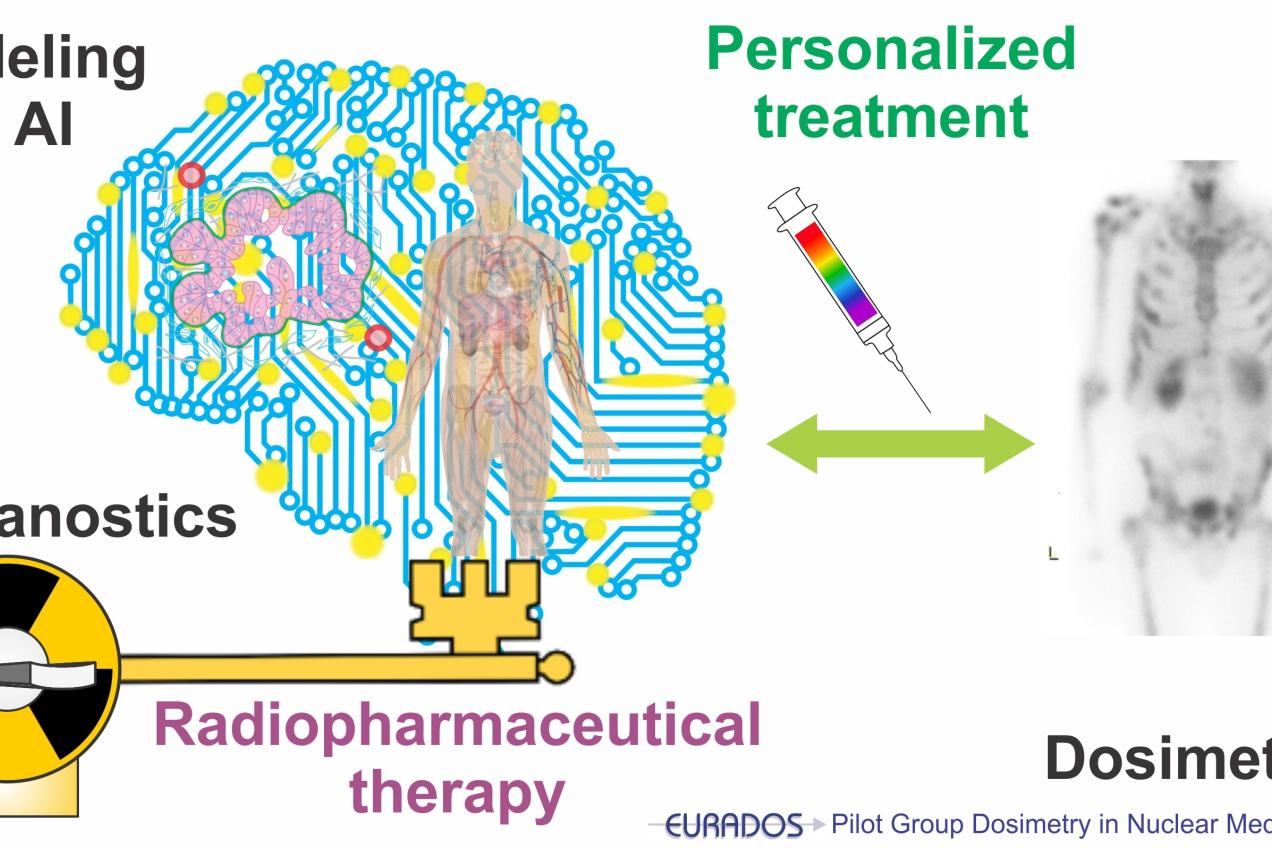
TG2 AI in pharmacokinetic modeling and dosimetry in nuclear medicine
Task Group leader: Kuangyu Shi (Universitätsspital Bern, Switzerland)
The objective of this task is to implement established AI techniques in the pharmacokinetic modelling and patient dosimetry, especially in the emerging radiopharmaceutical therapy. We are now working on a review on “AI practical application in dosimetry for radiopharmaceutical therapy” from a EURADOS view. In the same time, we are implementing and intercomparing machine learning algorithms in organ-level dosimetry prediction.
-
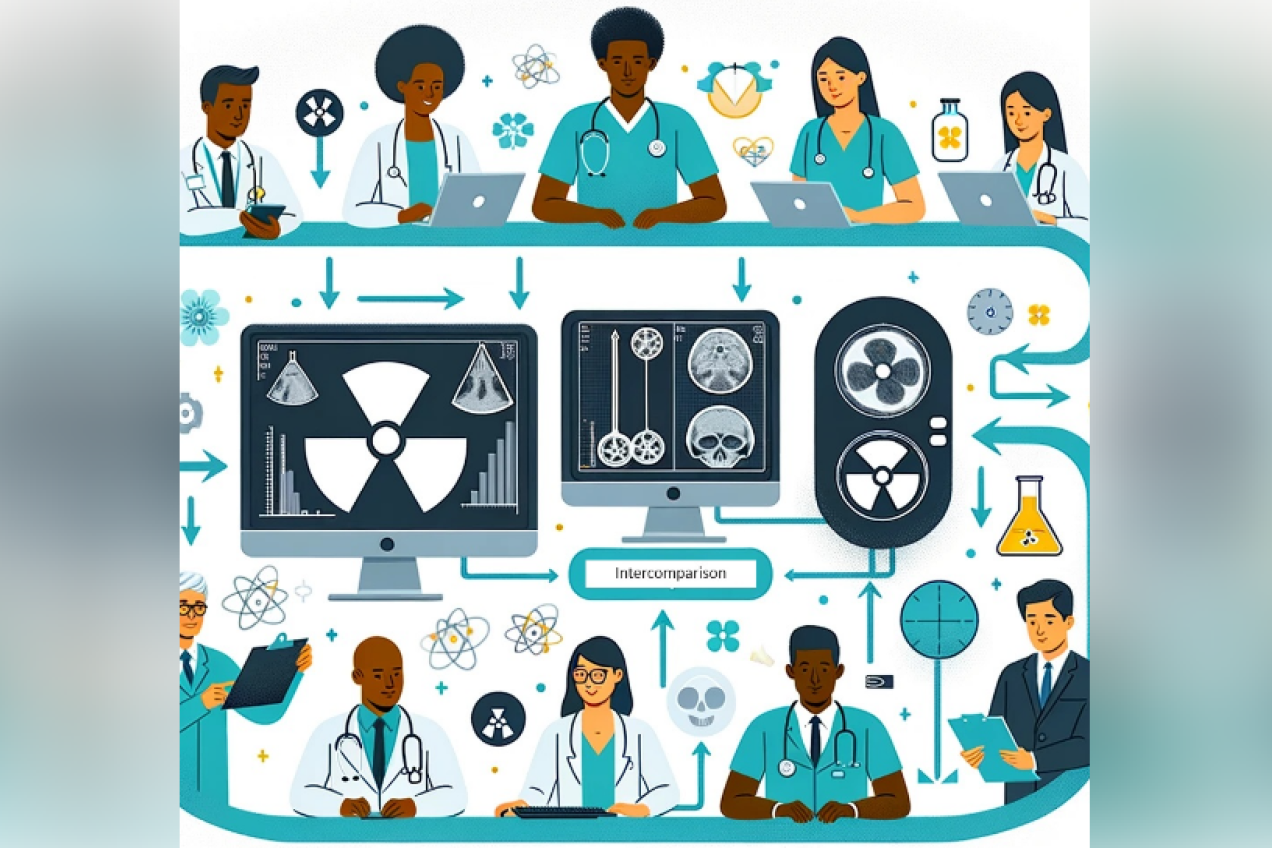

TG3 Intercomparison of radiopharmaceutical dosimetry in the clinical dosimetry community.
Task Group leader: Juan Ocampo Ramos (Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, USA)
Dosimetry intercomparison is important for evaluating and improving the accuracy and precision of radiation absorbed dose calculations, as well as for ensuring the safety and quality of nuclear medicine procedures. The task will try to identify the range of results and then investigate the origins of any potential discrepancies based on assumptions, methodologies, software, or tools used. Finally, the aim is to identify and develop EURADOS guidelines to harmonize clinical patient dosimetry in cooperation with other professional nuclear medicine associations.
-
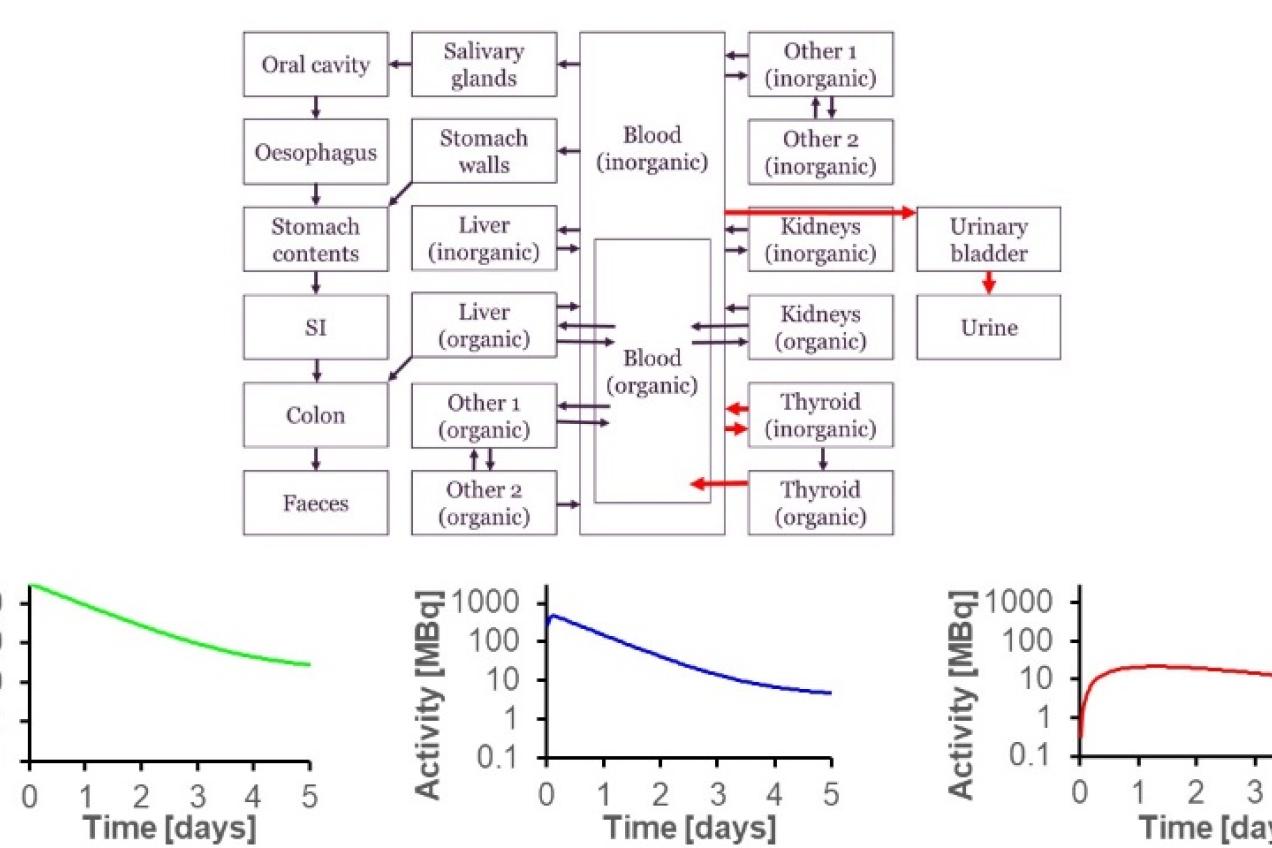
TG4 Disease-specific pharmacokinetic model and dosimetry for I-131 hyperthyroidism and cancer therapy
Task Group leaders: Maria Carapinha (ESTeSL, Portugal) and Jan Taprogge (Royal Marsden Hospital, UK)
ICRP biokinetic models often only consider healthy reference populations. Iodine biokinetics are expected to differ in hyperthyroid patients and revised biokinetics models are essential for radiation protection purposes. This task will aim to collate biokinetic information available in the literature and attempt to create a disease-specific model for patients with Grave’s disease.
-
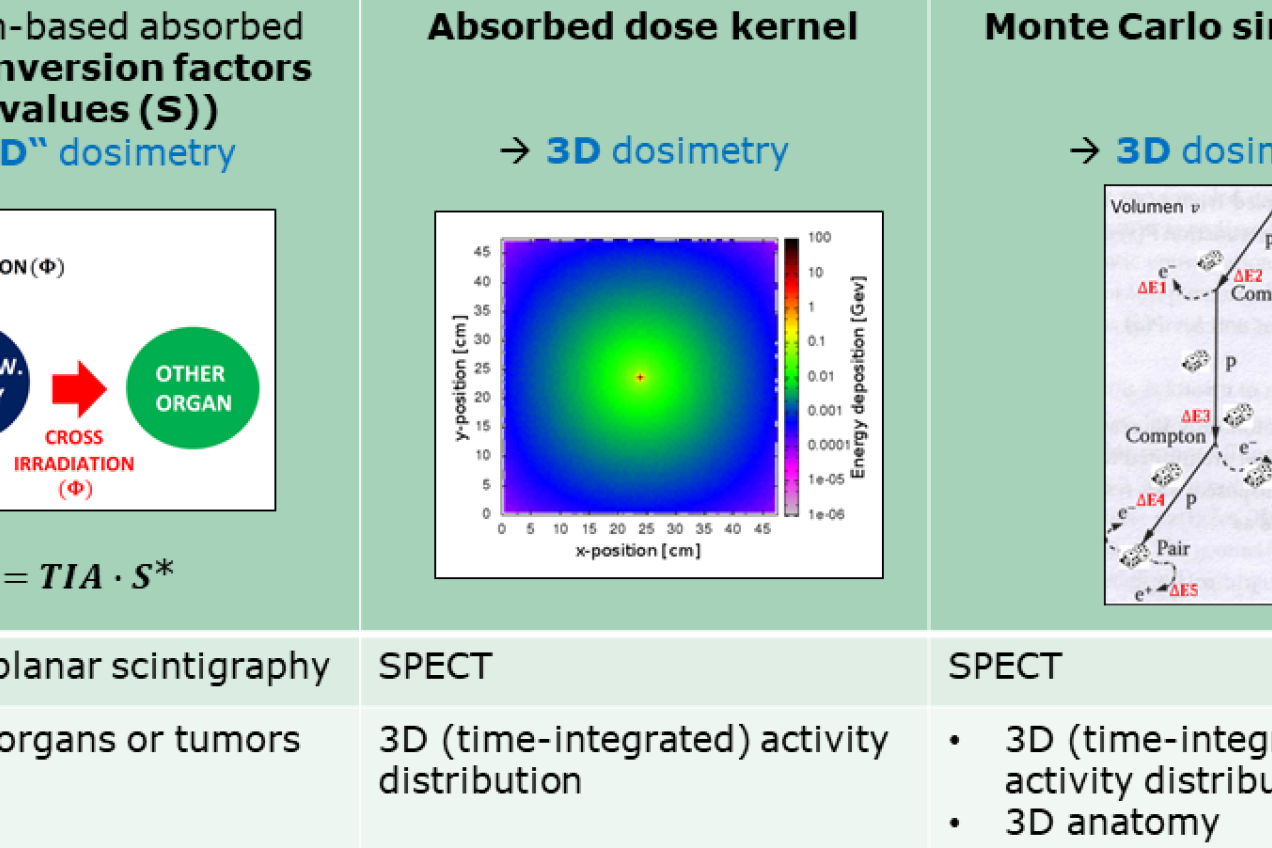
TG5 3D-dosimetry in clinical imaging and treatment planning
Task Group leader: Astrid Delker (Klinikum Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Germany)
This task will focus on 3D dosimetry techniques in normal organs and tumor. In addition, we will implement this technique to improve, for example, correlation between bone marrow toxicity and response in case of presence of bone metastases.
-

TG6 Small Scale Dosimetry
Task Group leader: Philipp Ritt (Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Germany)
This task will apply advanced dosimetric techniques which are based on in vitro and in vivo imaging technologies to assess absorbed doses in the sub-tissue and sub-organ level, such as kidneys and bone marrow.
-
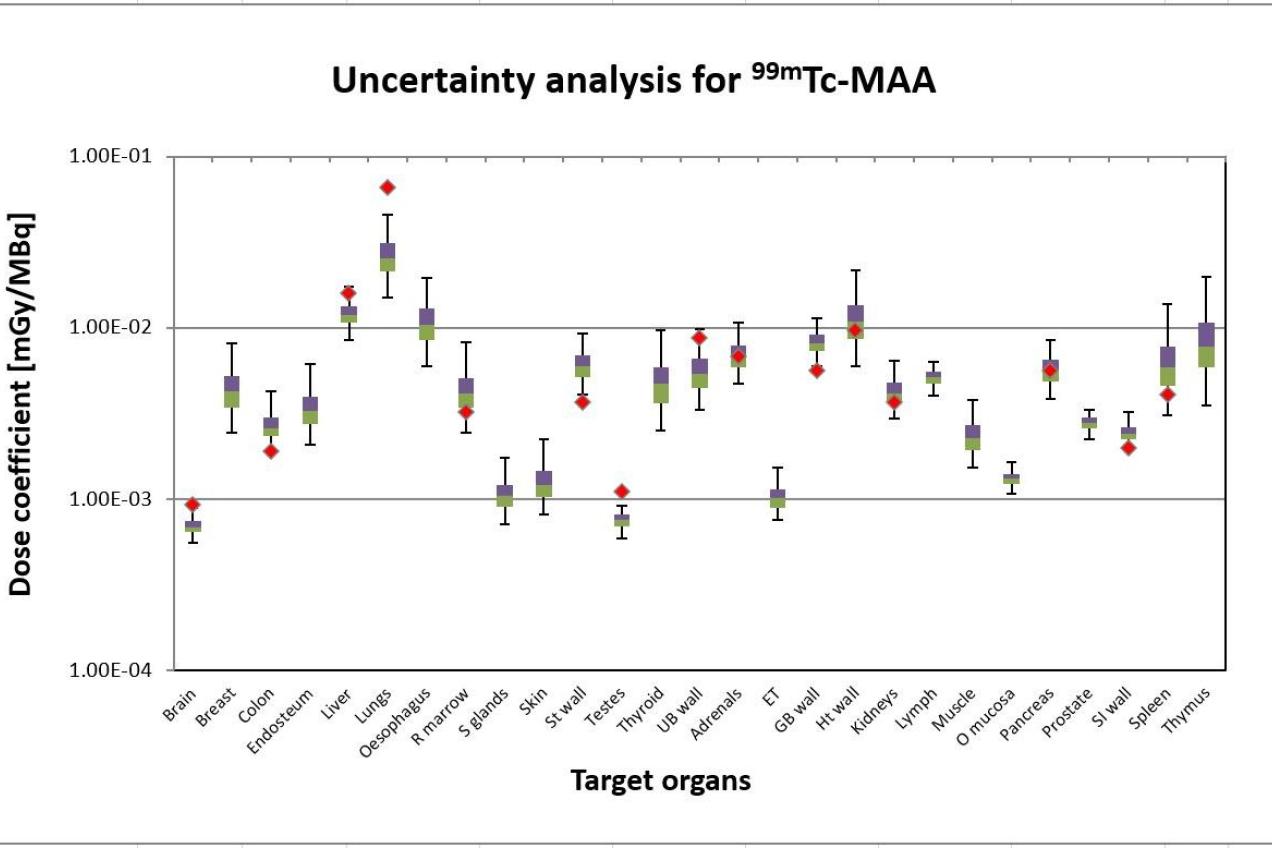
TG7 Uncertainty analysis in nuclear medicine dosimetry
Task Group leader: Vladimir Spielmann (BfS, Germany)
The absorbed dose coefficients to the patients from administered radiopharmaceuticals are usually calculated according to the generalized schema recommended by the MIRD and ICRP. In these calculations, the mathematic models for the time-dependent activity curves in organs and tissues (pharmacokinetic models) and the mathematic and digital representations of the human body (voxel phantoms) are initially evaluated. Because of the uncertainties in the image acquisition chains and the variability of the patients, the image-based pharmacokinetic models and the reference human phantoms used for the estimation of absorbed doses to patients are subject to large sources of uncertainty. Hence, for an individual patient, the resulting dose coefficients are uncertain. In this task, general methods and programs will be developed for assess the uncertainty of organ absorbed dose to patients in diagnostics and treatments, furthermore, sensitivity analysis approach will be applied for identify the important model parameters in the dose calculation chain.
