WG3 – Environmental dosimetry
-

Chairperson
Arturo Vargas
Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC), Spain
Email: arturo [dot] vargas [at] upc [dot] edu (arturo[dot]vargas[at]upc[dot]edu) -

Secretary
Maria Amor Duch
Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC), Spain
Email: maria [dot] amor [dot] duch [at] upc [dot] edu (maria[dot]amor[dot]duch[at]upc[dot]edu) -

Membership
Working Group 3 has:
- 30 full members from 15 countries
- 70 corresponding members
Motivation
The protection of the public against ionising radiation and radioactive contaminations caused by nuclear or other radiologically accidents may affect thousands of people. Following a radiological event, radiation protection authorities and other decision makers need quick and credible information on affected and contaminated areas. In March 2011, the nuclear power plant accidents in Fukushima Daiichi demonstrated the indispensable need for permanent and reliable environmental radiation monitoring.
In Europe, at present, more than 5000 stations make radiological monitoring data available in nearly real-time. In case of a nuclear emergency, national dose rate data have to be provided to the European Commission (EC) on an hourly basis, via the EUropean Radiological Data Exchange Platform (EURDEP). Based on these and other radiologically relevant data, the EC, which is in charge of the European Community Urgent Radiological Information Exchange System (ECURIE) may issue recommendations to the EU member states which could affect millions of people and may have severe economic and sociological consequences. In addition, the development of new detector systems based e.g. on LaBr3, CZT and CeBr3 detectors, which are able to provide ambient dose rate values as well as nuclide specific data on contamination levels in real time, are being installed in radiological networks and requires metrological support. Therefore, there is a need for the harmonization and standardization of spectrometric units on European scale. A subgroup of WG3 (WG3-SG1) has been working on the fulfilment of these requirements. This subgroup also deals with the use of UAVs equipped with appropriate detector systems for the measurement of ionising radiation with the aim to optimise measuring procedures.
Complementary to the use of active dosimetry or spectrometry systems, passive area dosimetry systems (e.g. TLD and OSL) are widely used for the monitoring of nuclear, industrial, medical and research installations in Europe. Since 2014, a subgroup of WG3 (WG3-SG2) is addressing this topic and will organise intercomparisons of passive dosemeters used in workplace and environmental radiation monitoring. Harmonization within Europe in this topic is one of the major goals due to different national traditions and experiences.
The COUNCIL DIRECTIVE 2013/59/EURATOM brings significant changes, with respect to the former Directive 96/29/Euratom, in terms of protection measures related to exposures due to the inhalation of radon progeny not only in work environments but also in dwellings. The member states had 4 years (deadline 2018) to implement these regulations in their legislation. In 2018 the subgroup WG3-SG3 is created with the main objectives to harmonize activities in the field of radon activity concentration measurements and related dose assessments and to provide support in the usage of the radon/-progeny dose conversion factors published by ICRP in dose assessment at homes and at workplaces.
Aim of working group:
Provide information about the correct measurement of ambient dose and dose rate and radioactivity concentrations for different scenarios.
The aim of WG3 is to provide information about the correct measurement of ambient dose and dose rate and radioactivity concentrations for different scenarios such as routinary emissions from nuclear installations, nuclear emergencies with local impact and nuclear disaster with transboundary implications, and also regarding natural radioactivity scenarios such as radon dosimetry based on activity concentration measurements.
WG3 will contribute by:
- Metrological support of the harmonisation process of early warning dosimetry network systems in Europe
- Stimulation of cooperation; especially between the Institute for Environment and Sustainability (IES) with regard to EURDEP (EUropean Radiological Data Exchange Platform) and EURADOS WG3 in the field of environmental radiation monitoring
- Organisation of intercomparison programmes
- Development and support the usage of methods for environmental dosimetry
- Investigation of the use of gamma spectrometry systems for environmental radiation monitoring
- Definition of standards; e.g. the publication of technical recommendations
Task Groups
-

SG1 - Spectrometry systems for environmental dosimetry
Task Group leader: Ulrich Stoehlker (BfS, Germany)
- WP1: “Methods for calculation of H*(10) of spectroscopy monitors”monitors”
- WP2: "Tools for spectrum analysis including energy re-calibration”
- WP3: “Harmonization of dose rate monitors and spectroscopy detectors including uncertainties”
- WP4: “Development or airborne spec detectors for UAV based systems including calibration procedures comparison exercises“
-
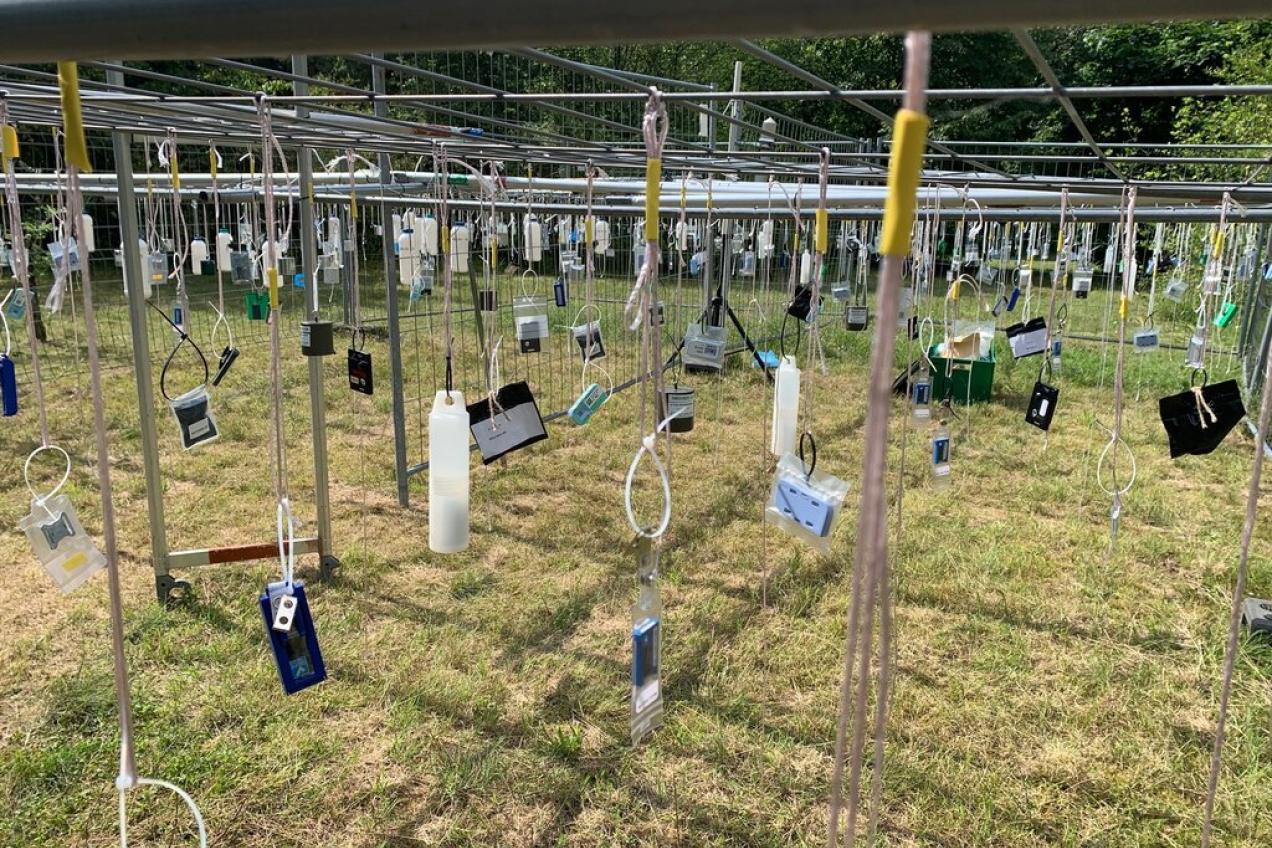

SG2 - Passive environmental dosimetry
Task Group leader: Christian Naber (KIT, Germany)
- Organisation of Intercomparisons on passive photon area dosemeters (e.g. IC2021area)
- Organisation of spectrodosimetry intercomparison IC2024spec
- Organisation of calibration Intercomparison IC2023calib
-
SG3 - Radon in metrology and field measurements
Task Group leader: Annette Röttger (PTB, Germany)
- Collaboration with traceRadon European Project (start in June 2020): climate change and radiation protection
- To provide support in the usage of the radon/ progeny dose conversion factors published by ICRP in dose assessment at homes and at workplaces: Collaboration between radon metrology (WG3) and radon dosimetry (WG7) in order to provide to the community guidelines and recommendations
