WG12 - Task Groups
Staff dosimetry (SG1)
-
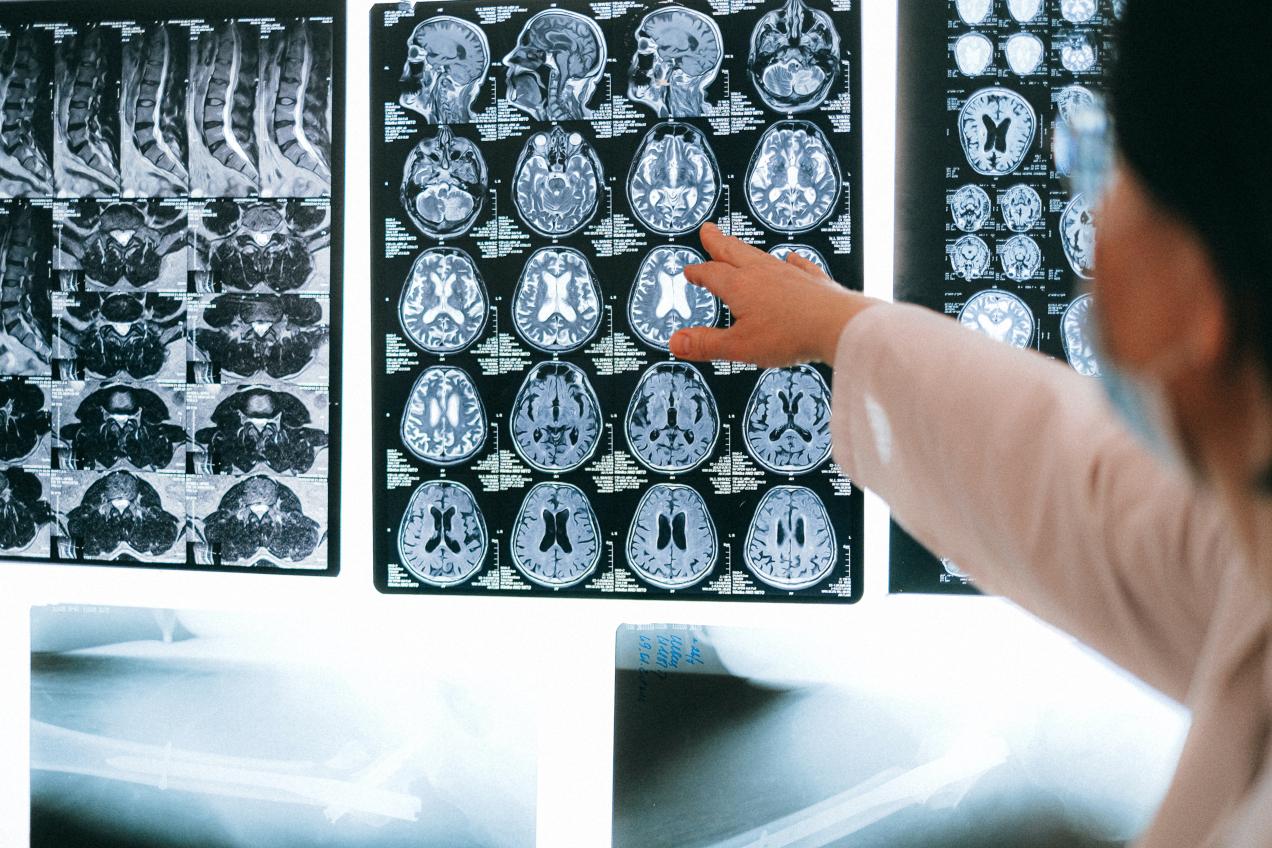
Task 1 - Report on individual monitoring in IR, general recommendations
Task leader: Isabelle Clairand (IRSN, France) and Eleftheria Carinou (GAEC, Greece)
The main aim of this task is to provide guidance on individual monitoring requirements in interventional radiology and cardiology workplaces. The recommendations that will be drafted will be addressed to employers, advisory bodies, radiation protection experts and officers, and health and safety services with main concern the radiation protection of workers in interventional workplaces in medical facilities.
-
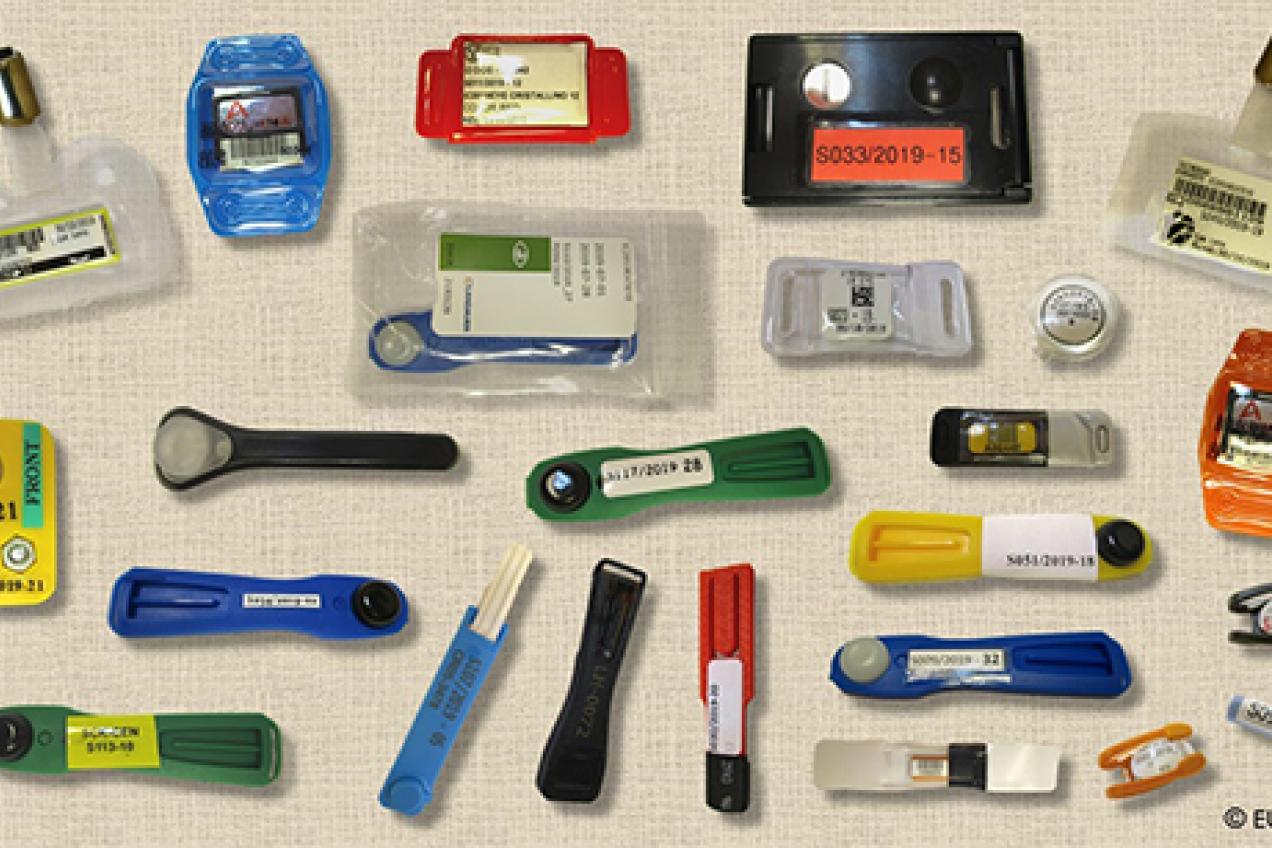

Task 4 - Intercomparison of eye lens dosemeters
Task leader: Isabelle Clairand (IRSN, France)
-
This task is carried out jointly with WG2 and consists in organising intercomparisons of eye lens dosemeters. This task is on hold, as there is no such intercomparison in progress at this time, but it can be reactivated when necessary.
This is a joint task with WG2 and WG12.
-
-
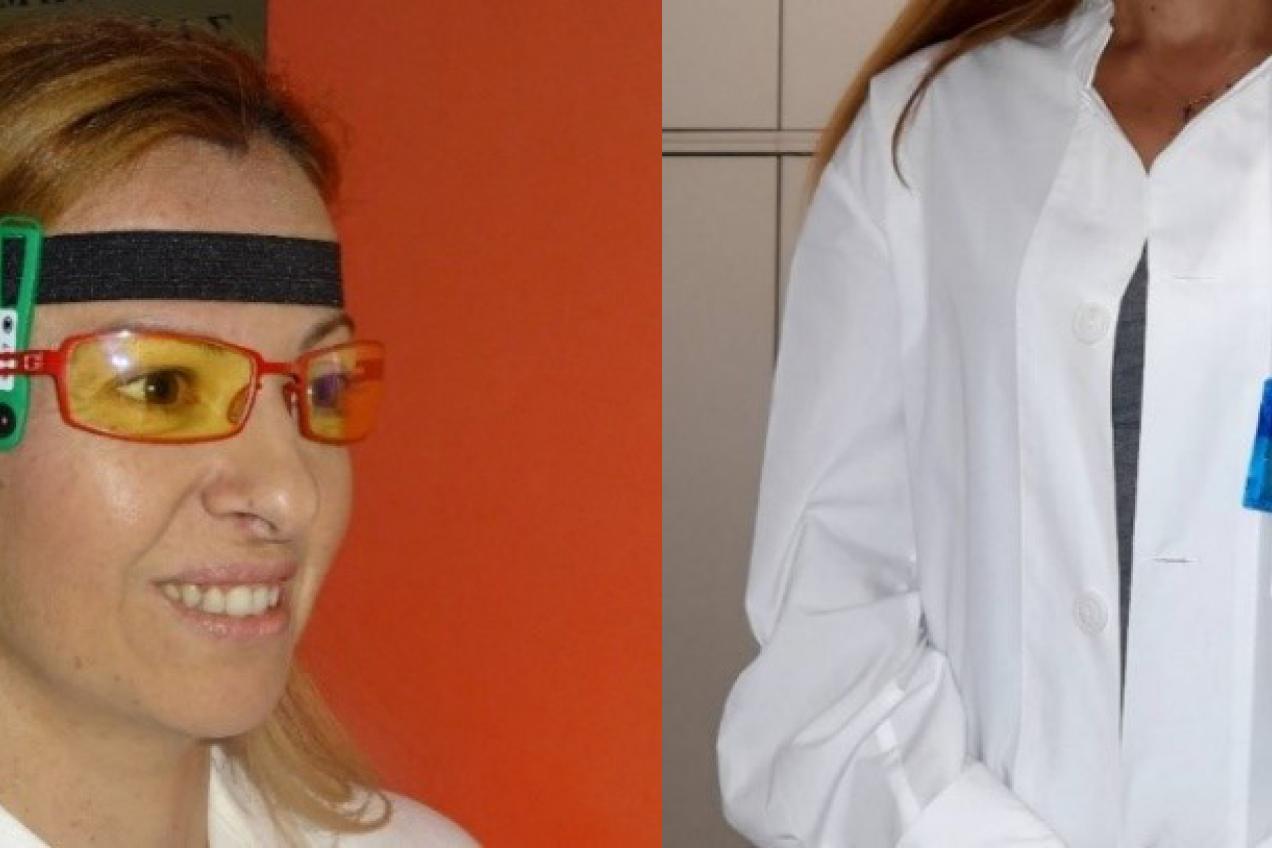
Task 5 - Eye lens dosimetry recommendations guidelines/double dosimetry
Task leader: Eleftheria Carinou (GAEC, Greece) and Mercè Ginjaume (UPC, Spain)
The main of this task is to prepare guidelines on matters of individual monitoring related to the use of algorithms for the estimation of the effective dose and the eye lens dose when radiation protection garments are used. The final action would be a technical note and an input to Task 1.
-
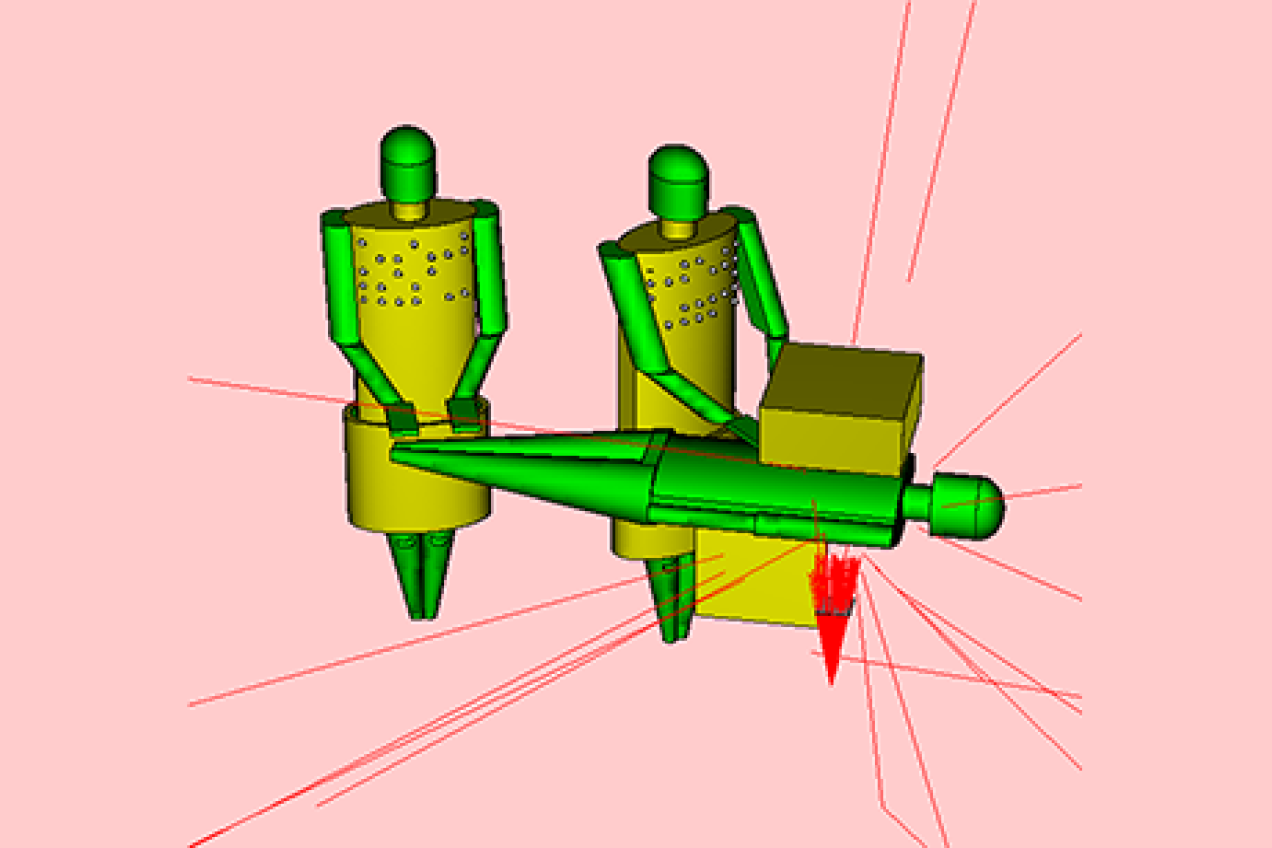
Task 7 - Doses received by personnel involved in complex interventional procedures
Task leader: Paolo Ferrari (ENEA, Italy)
The main purpose of this task is investigating the exposure of the medical personnel involved in interventional practices with numerical simulation, possibly validated through measurements. The simulations allow to better characterize the various aspects of irradiation condition of the different parts of the operators body (protected and unprotected by radiation protections tools) and to relate them to the dose monitoring, providing information to Task 1.
-
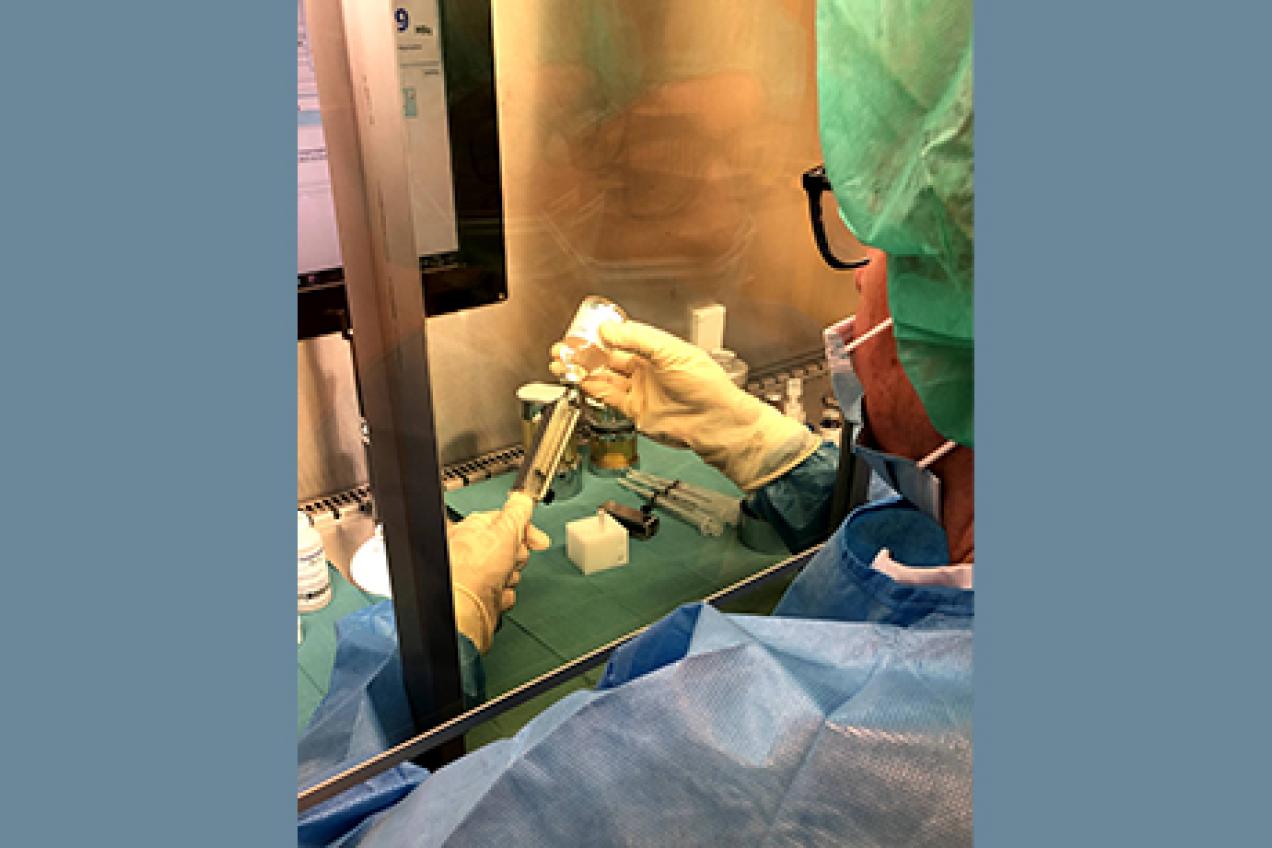
Task 8 - Extremity doses in nuclear medicine focussed on the new radionuclides
Task leader: Robert Kollaard (NRG, The Netherlands)
The purpose of this obtain an overview of the exposure of the extremities due to preparation, dispensing and administration of radiopharmaceuticals in nuclear medicine. The task is divided in a review and two questionnaires to gain insight in the current status of on one hand and is on the other hand investigating the exposure of the fingers due to the use of new radionuclides such as 68Ga and 177Lu.
-
Task 9 - Occupational exposure during the management, preparation and administration of "new" radiopharmaceuticals
Task leader: Paolo Ferrari (ENEA, Italy)
-
New radiopharmaceuticals for nuclear medicine theranostic practices, that combines therapy and diagnostic applications, are getting available in the market and their number is expected to increase in the future years. The main purpose of this task is investigating the exposure of the personnel and the public associated to their preparation and their administration to the patient.
This is a joint task with WG6, WG7 and WG12.
-
Patient dosimetry (SG2)
-
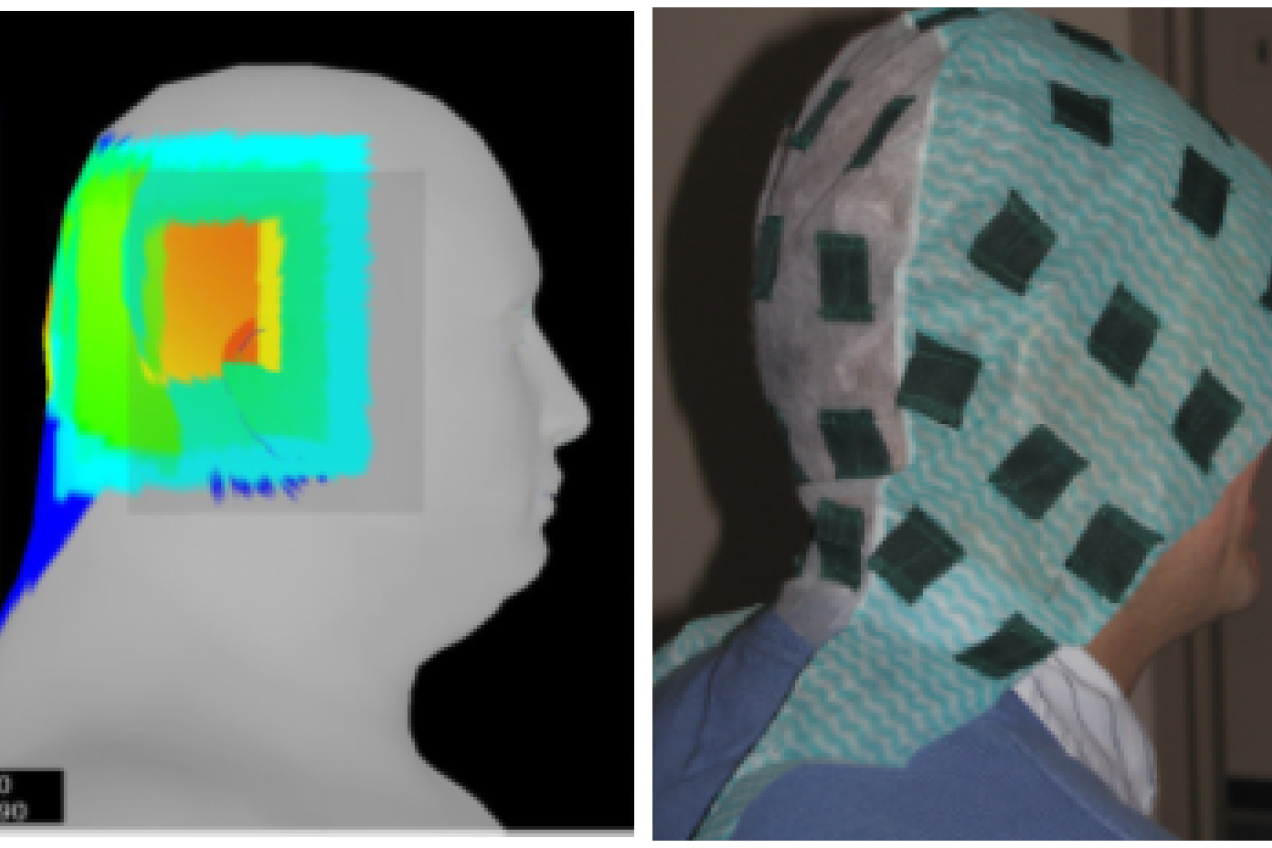
Task 1 - Skin dose in interventional radiology
Task leader: Jérémie Dabin (SCK CEN, Belgium)
The purpose of this task is to investigate the effect of various clinical and technical parameters on patient exposure during interventional procedures. The focus is currently on neuroprocedures; however, the data collection is currently on hold due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the difficulties to access the hospitals.
-
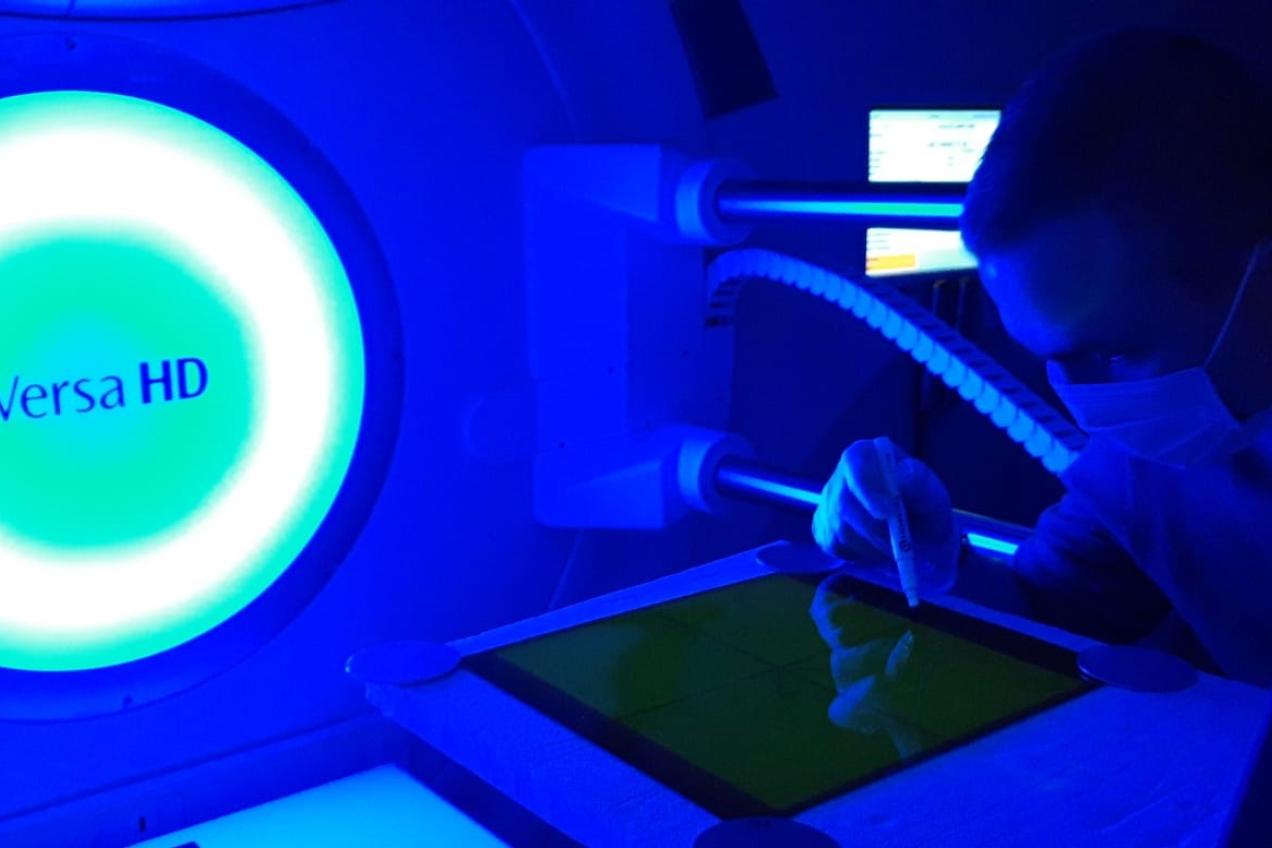

Task 2 - Personalized dose in radiotherapy
Task leader: Teemu Siiskonen (STUK, Finland)
-
Methods to calculate patient organ and effective doses in real patient anatomy are developed in this task. More specific tasks include the characterization of radiotherapy imaging devices, surveys of imaging frequencies and protocols (together with IAEA and ICRP), assessing the patient exposures using experimental and computational methods and producing good practice guides and recommendations for radiotherapy imaging (together with EFOMP).
This is a joint work between WG6, WG9 and WG12 and EFOMP.
-
-

Task 3 - Review of guidelines/recommendations on use of out-of-field shielding in X-ray imaging
Task leader: Marta Sans Merce (University Hospital of Geneva, Switzerland)
-
The purpose of this task is to review current recommendations and legislative documents on the use of out-of-field patient-contact shielding, including those from national authorities, international and national organisations and professional bodies.
Task is already finished and work is published.
-
-
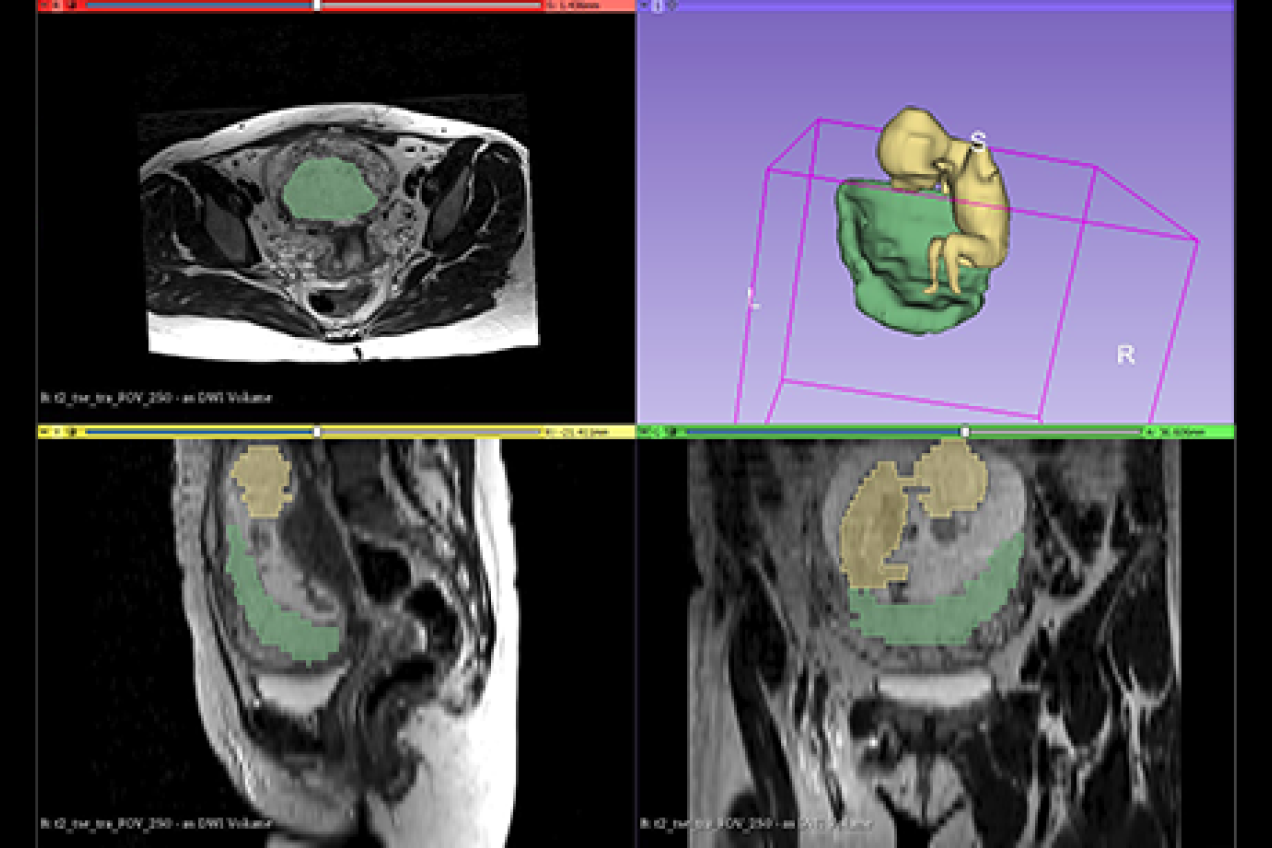
Task 4 - Dosimetry in pregnancy
Task leader: Dario Faj (Medical Faculty Osijek, Croatia)
To review, validate and compare different approaches for dosimetry in pregnancy related to medical exposure for all ionizing radiation modalities used in imaging (diagnostic radiology and nuclear medicine). The task started with a literature review and a questionnaire to gain insight in the radiation protection considerations and dosimetry approaches used. It will be followed by assessing the pregnant patient exposures using experimental and computational methods in different clinical settings.
-
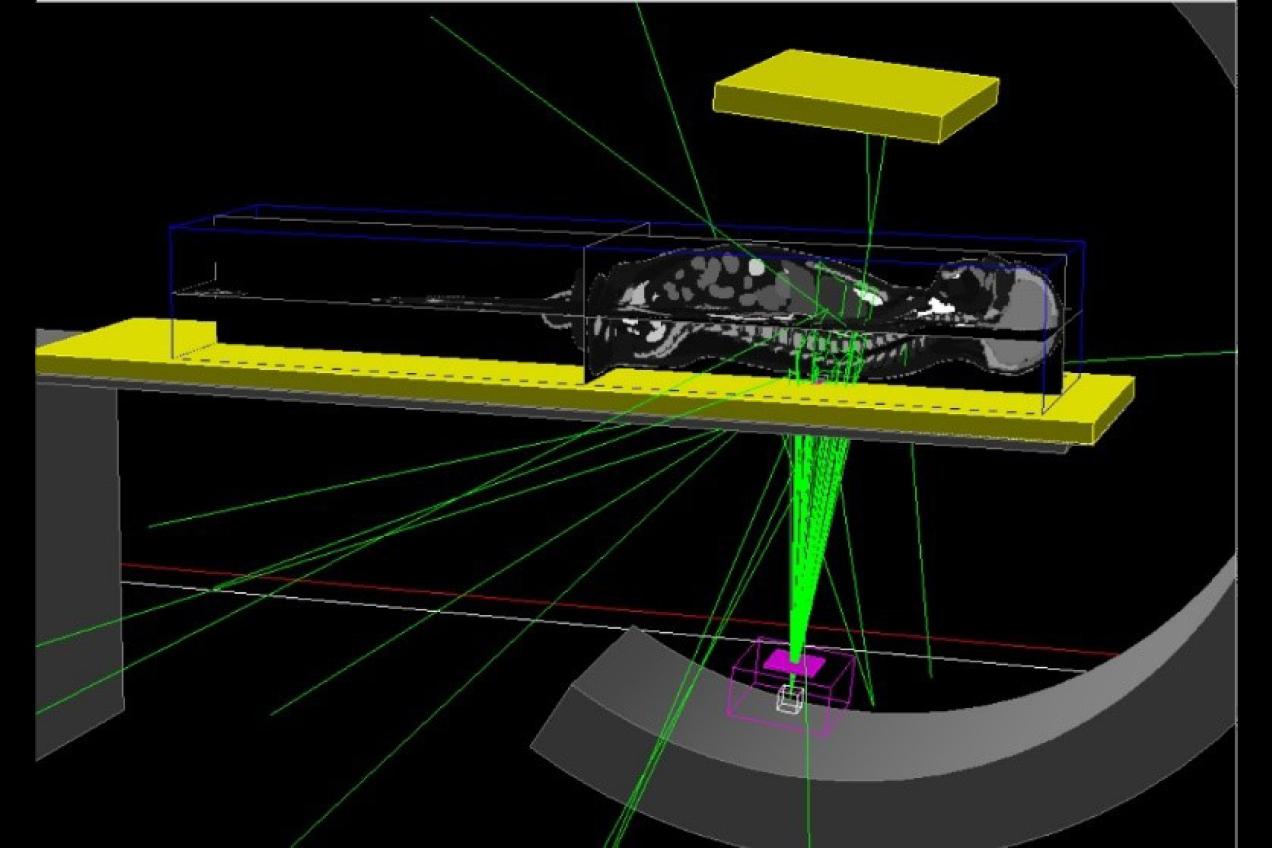
Task 5 - Organ doses in interventional radiology
Task leader: Nicolas Arbor (University of Strasbourg, France)
-
This task is interested in the issue of the accuracy and reliability of organ dose estimate in interventional radiology. The main purpose is to characterize the variability of measurements and calculations depending on the different parameters that can affect the dose reconstruction (DICOM RDSR data, manufacturers, dosimetry tools, …).
